Build AI Agents with LangChain:- Have you ever wished you had an assistant who not only answers your questions but also does things for you? Like, doing research on the internet, analyzing data, or drafting emails for you?
We are not just talking about chatbots like ChatGPT or Google Gemini. We are talking about AI Agents – AIs that can think, plan, and take action.
If you are a developer or have an interest in technology, then there is good news for you. Creating AI Agents is no longer rocket science, and the credit goes to LangChain.
Today in this article, we will understand in a very simple way what these AI Agents are, what LangChain is, and how you can use it to create your own AI Agents. So let’s get started!
What is AI Agent?
Let’s take an example to understand this.
You ask a normal chatbot, “What is the capital of France?” It will immediately answer, “Paris”.
Now you ask an AI Agent, “What is the capital of France and make a list of the 5 best tourist spots there and give me a table with their today’s ticket price.”
Now the game changes here. A normal chatbot will not be able to do this. But what will an AI Agent do:
- Reasoning: “Okay, I have to do two things. First find out the name of the capital, then find 5 tourist spots, and then find out their ticket price.”
- Planning: “I will first find the capital using Google Search. Then I will use the API of a travel website to get the top spots and their ticket prices. Finally, I will arrange all this information in a table.”
- Take action: It will actually use these tools (Google Search, API), gather information, and give you a final answer.
In short, an AI Agent is a program that uses a Large Language Model (LLM) like GPT-4 as a “brain” and connects it to “tools” from the outside world to get the real work done.

Introducing LangChain: The Magic Lamp of AI Agents
So now the question is how do we connect LLM (brain) to these external tools (hands and feet)? This is where LangChain enters like a hero.
LangChain is an open-source framework (i.e. a set of tools) that helps developers build applications based on LLM.
It is not an AI model, but it acts as a bridge that connects your AI model to things in the outside world like databases, APIs, and the internet. Without LangChain, your LLM is like a very knowledgeable person who is locked in a room. LangChain gives him the power to get out of that room and interact with the world.
Why choose LangChain?
- Modular: You can choose and connect different parts (e.g. which LLM, which tools) according to your needs.
- Ready-Made Components: It comes with pre-built components like agents, tools, and memory, which saves you a lot of time.
- Powerful: It gives you the freedom to build anything from simple chatbots to complex reasoning agents.
- Strong Community: Its community is very large and active, so you can easily find help and resources.
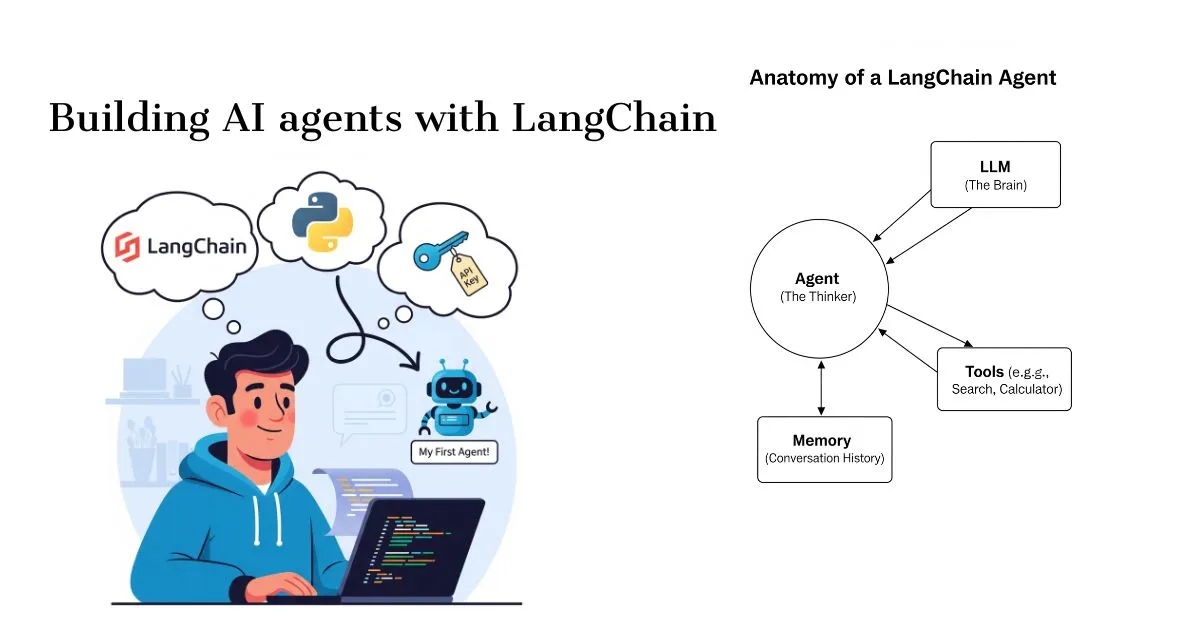
Anatomy of an Agent
LangChain uses some main building blocks to build an AI Agent. It is very important to understand them.

1. LLM (The Brain)
This is the core engine of your agent. It could be OpenAI’s GPT-4, Google’s Gemini, or another open-source model. It does all the thinking and language processing.
2. Tools (The Superpowers)
Tools are the functions your agent can use. They could be anything:
- Google Search: To find anything on the internet.
- Calculator: To solve math problems.
- Python REPL: To run code and see its output.
- Database Access: To retrieve information from your company’s database.
- API Calls: To fetch weather information, stock market data, or data from any service’s API.
You can even create your own custom tools!
4. Agent (The Decision Maker)
This is the real wizard. The agent’s job is to coordinate between the LLM and the tools. When you give the agent a task, it asks the LLM, “What tool should I use to do this task?” The LLM replies, “Use Google Search”. The agent then runs the Google Search tool, gets its output, and asks the LLM again, “What to do now?”
This process continues until your task is done. ReAct (Reason + Act) is one of the most popular agent logics.
4. The Memory
What if your assistant forgets everything every time it talks to you? Wouldn’t be fun, right? This is where memory comes in handy. Memory helps your agent remember past conversations. This allows it to better understand your questions and continue the conversation.
Let’s create a simple agent: Step-by-Step concept
We won’t write the full code here, but will give you an idea of what the process looks like.
Mission: Create an agent that can tell the capital of any country and solve a simple math problem.
Step 1: Setup
First, you need to install Python, LangChain library, and OpenAI (or any other LLM provider) library on your computer. You will also need an API Key.
Step 2: Choose your LLM
You will tell LangChain that you want to use OpenAI’s gpt-3.5-turbo model.
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0)
Step 3: Define your Tools
Now we will create two tools for our agent:
- A tool that can search the internet (LangChain has a built-in tool for this called SerpAPIWrapper).
- A tool that can do math (LLMMathChain is for this).
tools = [Tool(name=”Search”, func=search.run, …), Tool(name=”Calculator”, func=llm_math.run, …)]
Step 4: Initialize the Agent
Now we’ll tie all of this together. We’ll tell LangChain who our LLM is, what our tools are, and what agent type (e.g. zero-shot-react-description) we want to use.
agent = initialize_agent(tools, llm, agent=AgentType.ZERO_SHOT_REACT_DESCRIPTION, verbose=True)
Step 5: Run the Agent
Now you can ask your agent questions:
agent.run(“What is the capital of Japan, and what is 25 * 5?”)
What happens next:
- The agent will think: “I have to do two things. First find the capital of Japan, then multiply 25 by 5.”
- First action: He will use the “Search” tool and search for “Capital of Japan”. The output will be “Tokyo”.
- Second action: Now he will think, “The first task is done. Now I have to do 25 * 5.” He will use the “Calculator” tool. The output will be “125”.
- Final answer: The agent will combine both answers and give you: “The capital of Japan is Tokyo and 25 * 5 is 125.”

Uses of AI Agents in the real world
It’s not just a fun toy. Companies and developers are already using it:
- Smart customer support: Agents who don’t just answer questions, but can also go into a user’s account and process a refund or change the status of an order.
- Personal research assistant: Agents who spend hours researching the internet and create a summary report for you.
- Automated data analysis: You upload your CSV file and tell the agent, “Tell me the sales trend in this data.” He will analyze the data on his own and give you graphs and insights.
Conclusion:-
The era of AI Agents has just begun, and LangChain is making it accessible to every developer. It is transforming LLMs from mere talking parrots to thinking and working assistants.
Building AI agents with LangChain is no longer a thing of the future, but a reality today. If you want to build something big and impactful in the world of AI, learning LangChain can be a game-changer for you. So why wait? Check out its documentation today and take the first step towards building your first AI agent!
Read more:-
what is genspark ai, genspark ai review A Comprehensive Guide for 2025
Quack AI Governance: Transforming the Future of Blockchain Decision-Making
5 best ai tool for coding free That’ll Level Up Your Coding in 2025